|
In 2009, I received the Japp Bakema Fellowship from the Netherlands Architecture Institute for my project ZERO. It was the height of the Great Recession and architects were laid off by the droves daily in Chicago. My architecture students who recently graduated were unable to find work or had to take up odd jobs to make ends meet. As an architect and a teacher, I came to realize the limitation of an architectural education that resides within an academy and cut off from the larger society, which architecture students will eventually be part of. I was dismayed by the narrow definition of architecture, the limited contributions of an architect besides a building, and the traditional client-architect relationship in practice. I saw the Great Recession as an opportunity to re-evaluate and re-frame architecture education and the role of an architect in society.
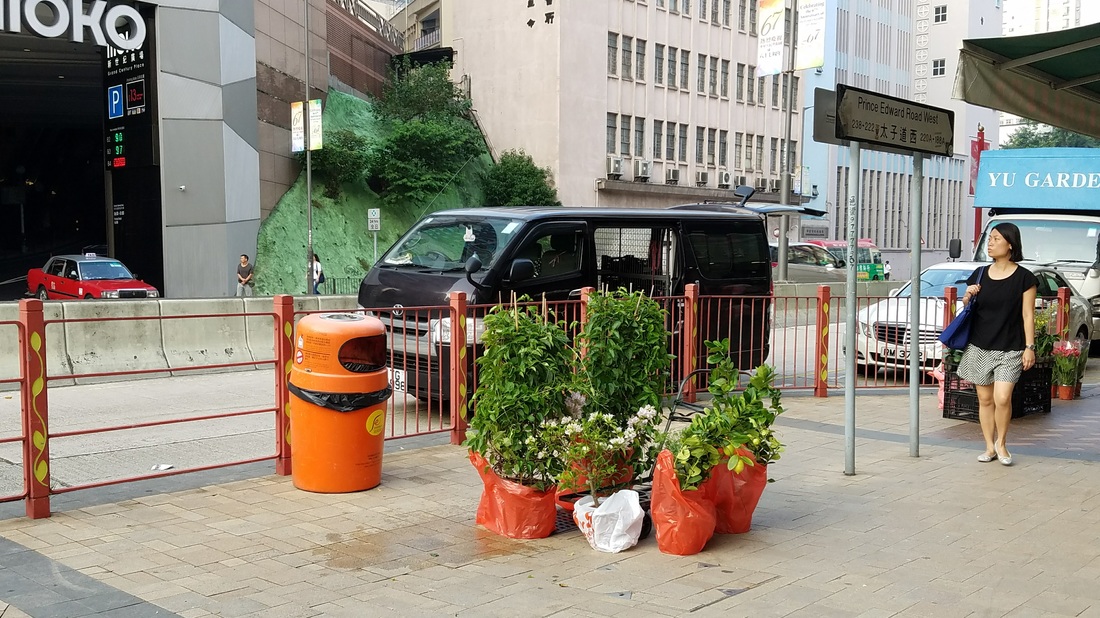
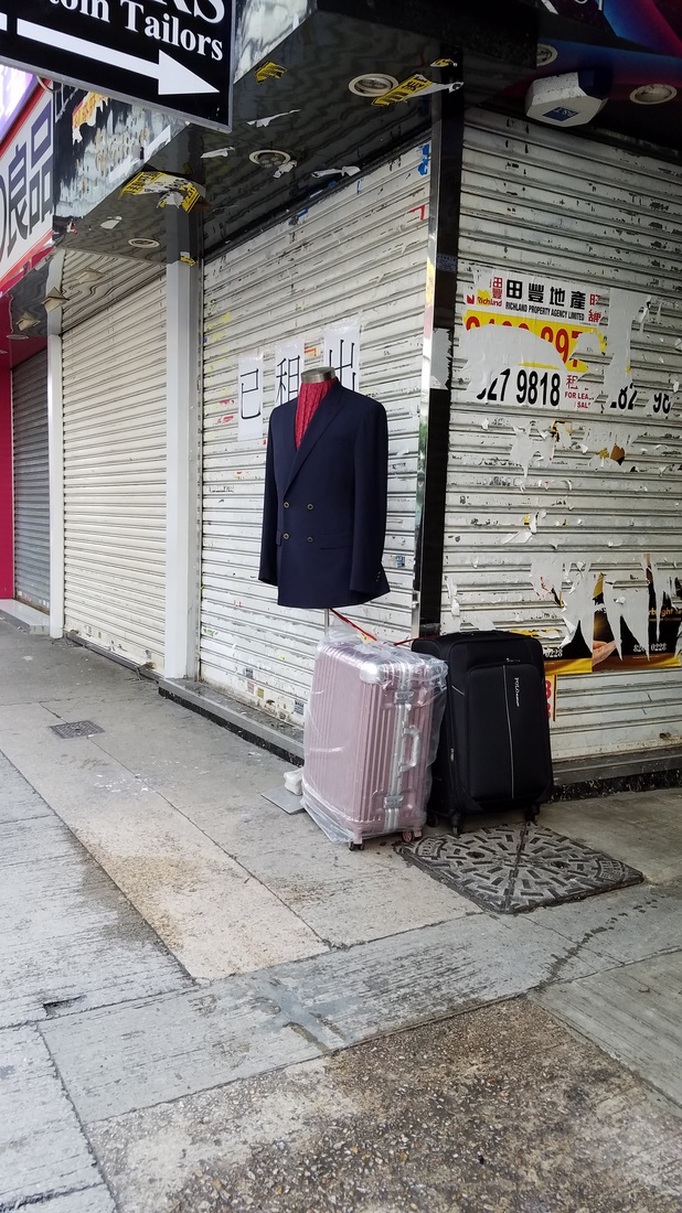
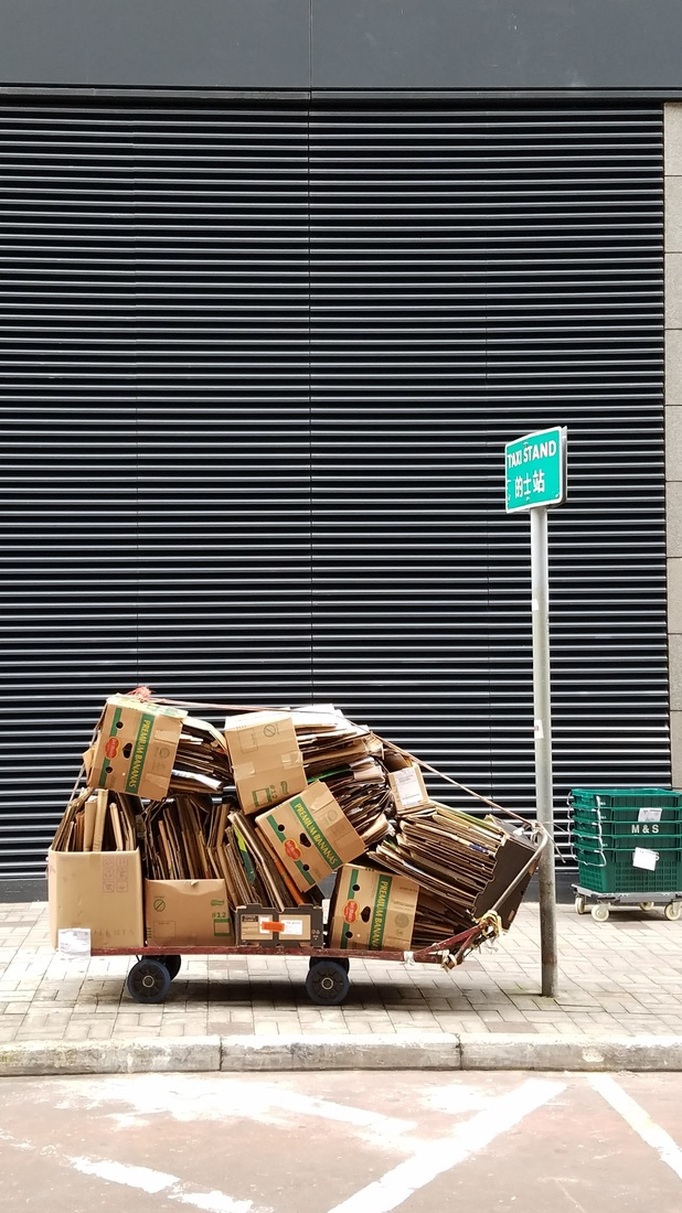
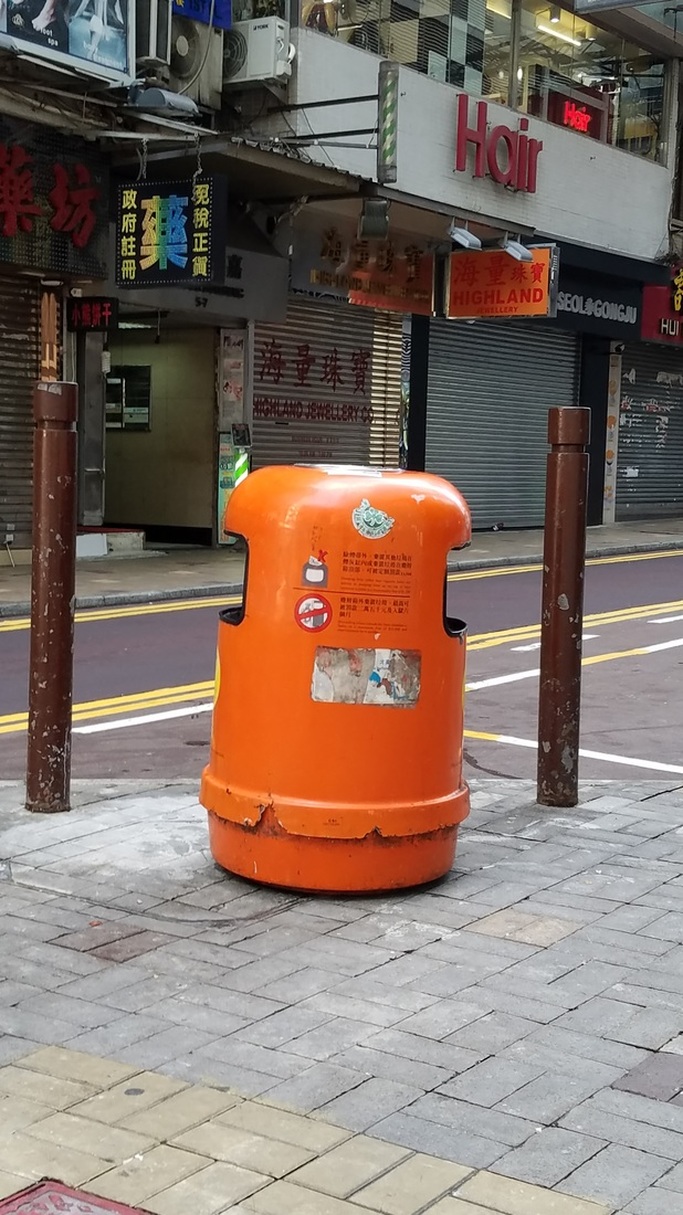
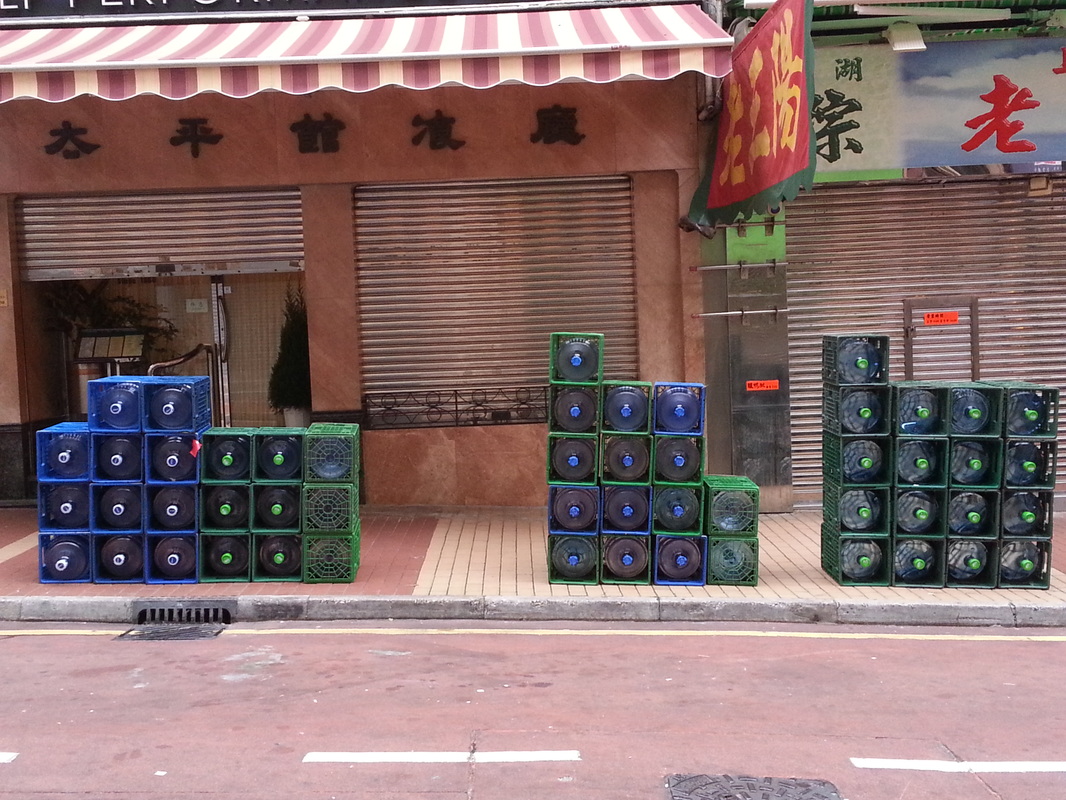
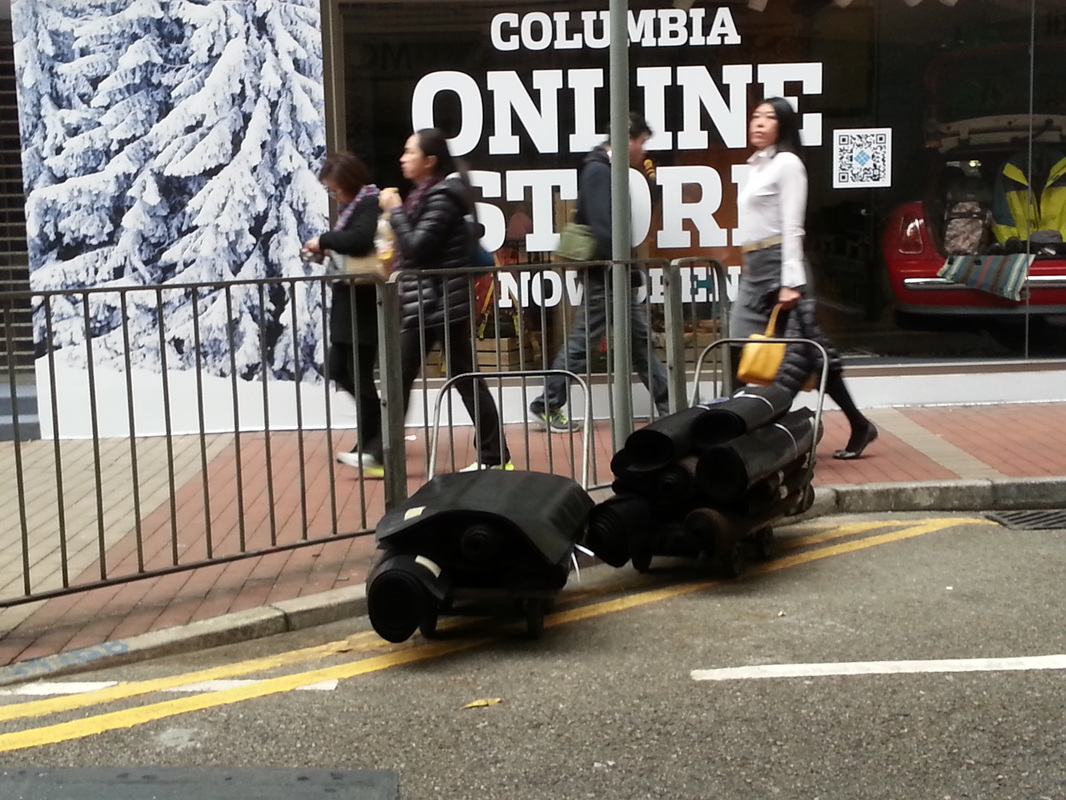
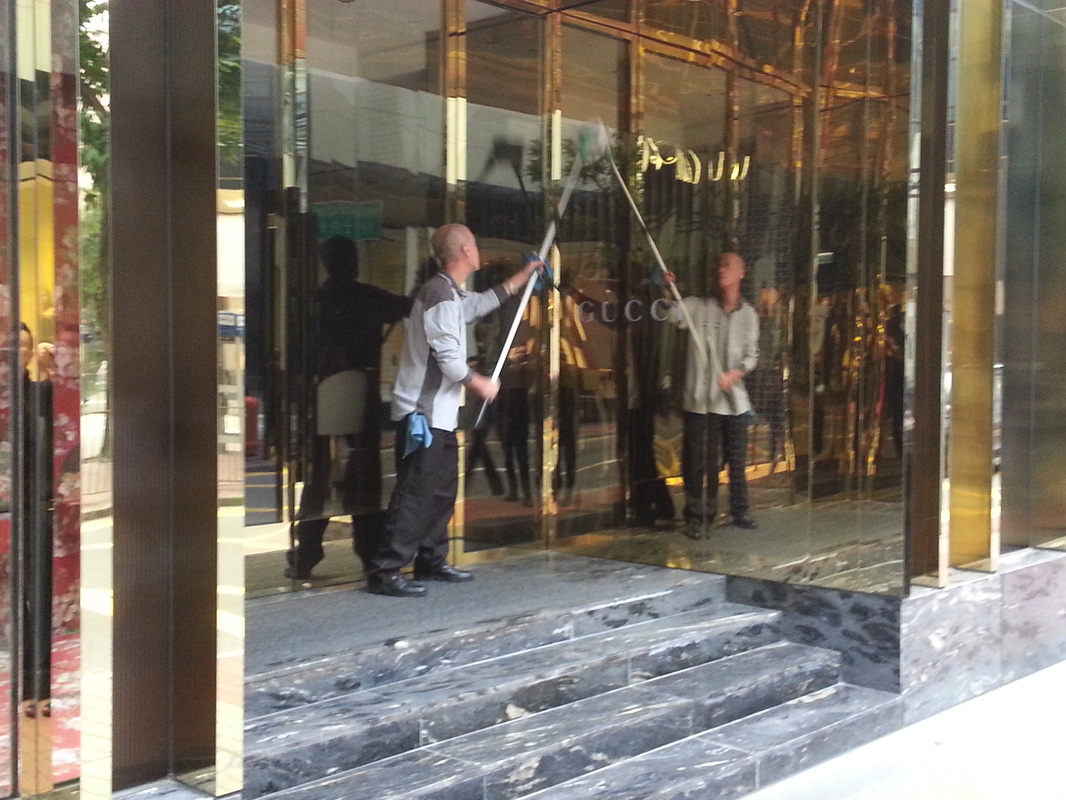
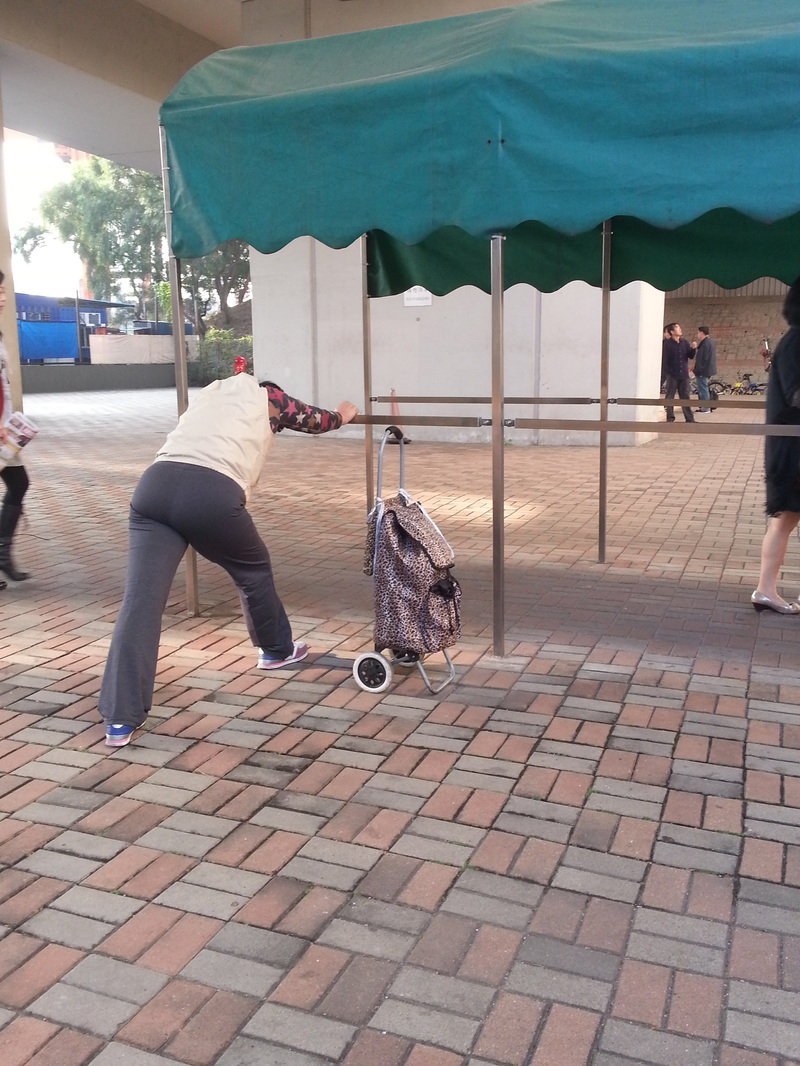
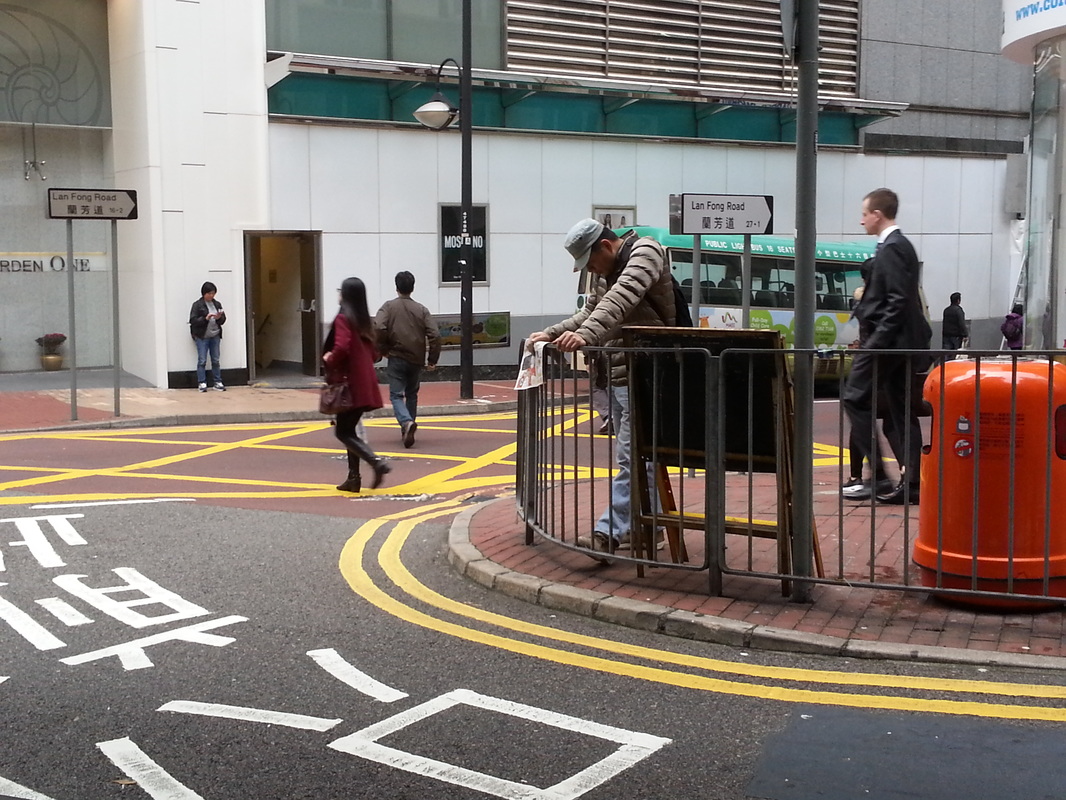
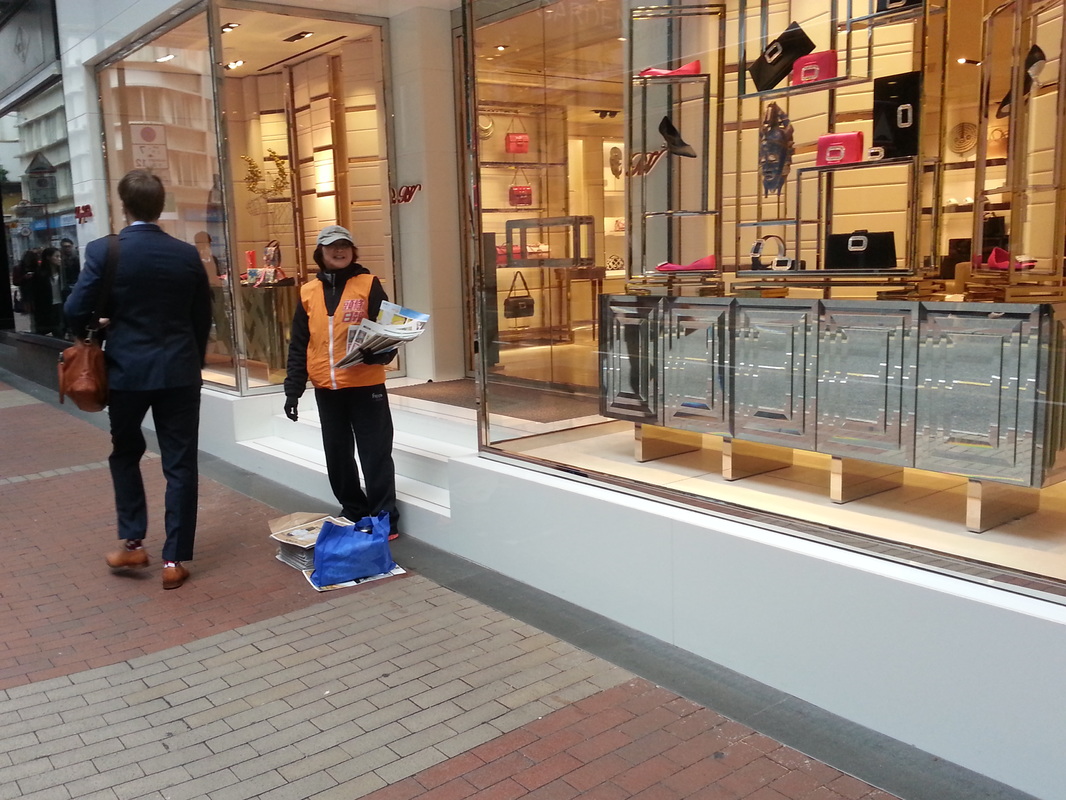
The fellowship afforded me the financial resources and time to research and document the various manifestations, causes, and meanings of emptiness, the values of unbuilding and how the local residents in Asian cities, many who were living along the margins of society, were able to occupy empty spaces for different durations and for social, commercial and personal uses. It opened my eyes to their ingenious, opportunistic, and informal use of empty spaces, found materials and urban infrastructures to fulfill their daily needs. Through ZERO, I discovered the relational dynamics of their occupations and actions, which were attributed to their creative use of scarce resources, and their ability to adapt, negotiate and utilize social relationships and existing spatial contexts to their advantage. Their occupation tactics were both a form of resistance and an adaptation to the planned spaces in the cities. I was fascinated by the spatial intelligence and material resourcefulness of the residents despite not receiving any formal design education. Its radical design amateurism and material relativism driven largely by pure purpose and need challenged what I learned in architecture school and the canons of good design. ZERO discovered the under and unrepresented everyday beauty and the potentiality of society’s detritus, be it material, social, cultural or spatial. The casual juxtaposition of the planned and spontaneous, the new and the discarded questioned our conventional notion of authenticity. The creative re-using of cast-off objects and materials by the residents was also a consoling knowledge in an age of throw-aways. ZERO was a timely springboard for my own search for an alternative design education and practice at a time of economic crisis, as well to broaden what an architect can contribute to society besides another building in a post-economic bubble age. The city is filled with people engaged in a wide variety of daily activities every morning- going to work, buying breakfast along the way, delivering goods and services, cleaning the shop front, waiting for the bus, etc. These activities occur repeatedly each day without fail, to the point of being involuntary like breathing. But their repetitions also instilled a sense of dullness and monotony. What happens when we reframe these ordinary activities as various forms art, ranging from public sculptures to performances? Will we begin to see and value them differently? Taken from Hong Kong one morning, the various objects and human activities reveal the rhythm and relationship of space, objects and people in the fast- moving city.
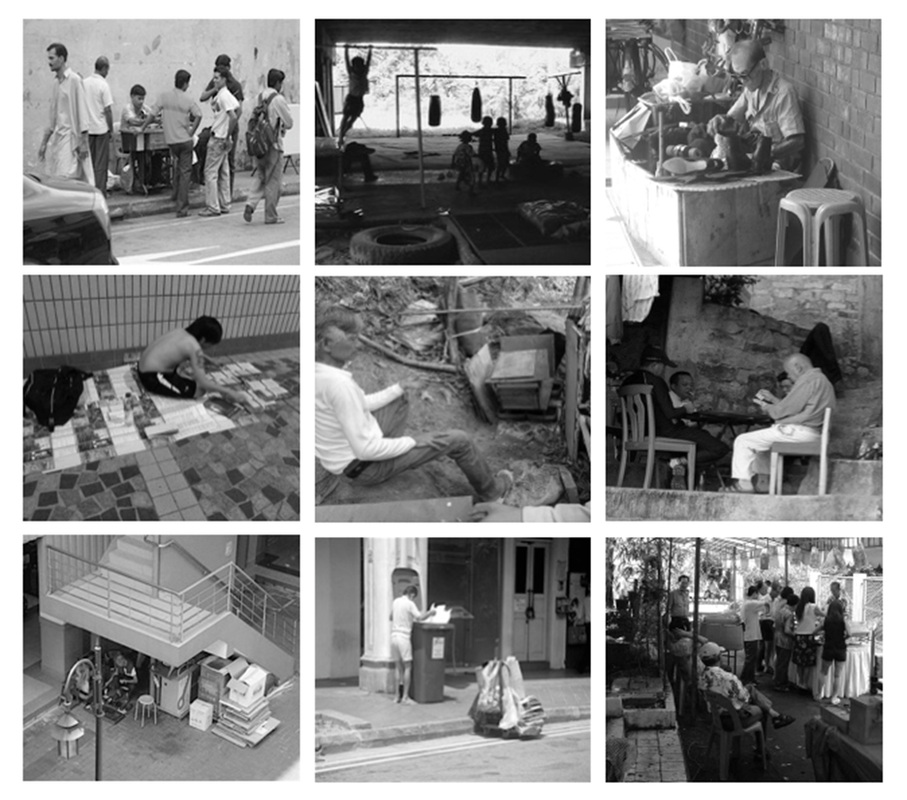
A selection of field notes taken during my multi-year research on the lives of urban dwellers living along the margins of society in Asian cities.
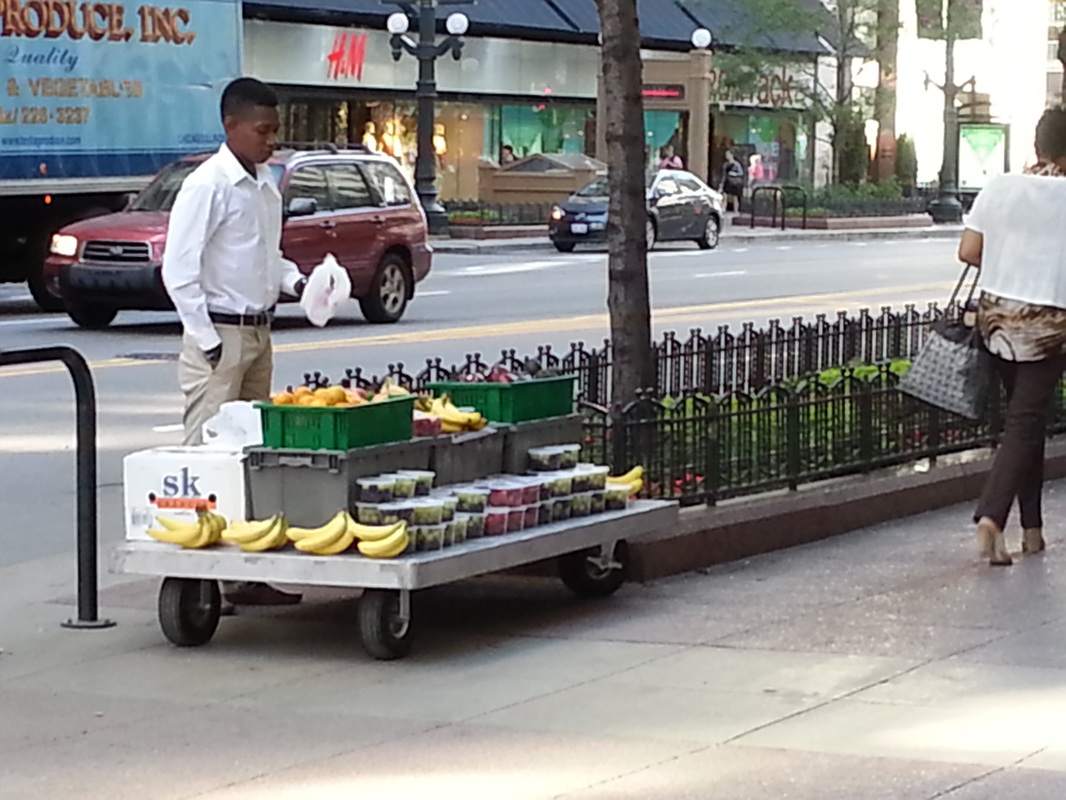
A wonderful sight on the way to work! A street vendor selling fresh fruits on the sidewalk. Summer is here, finally.
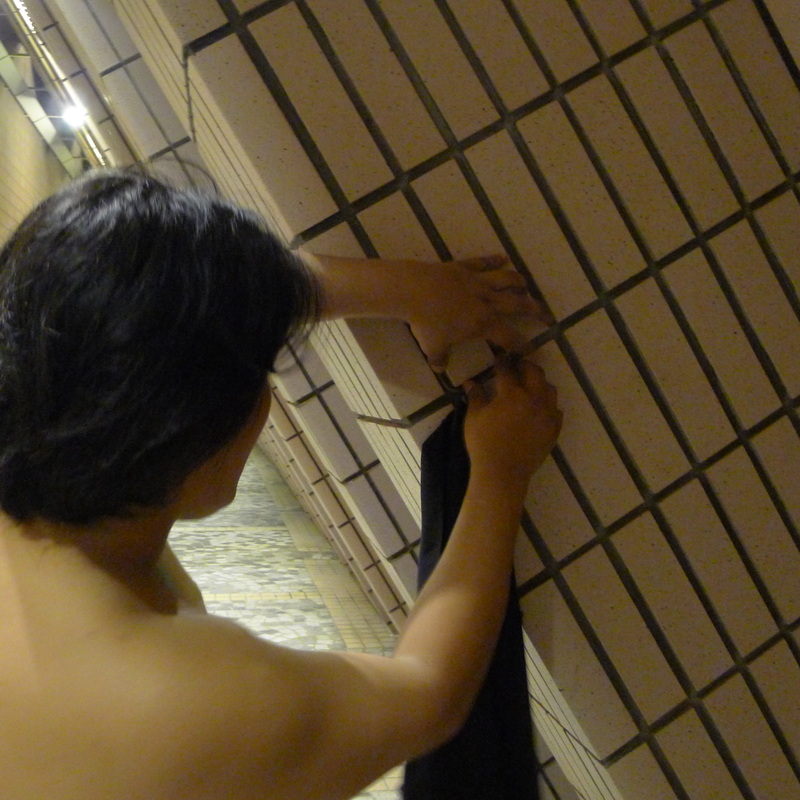
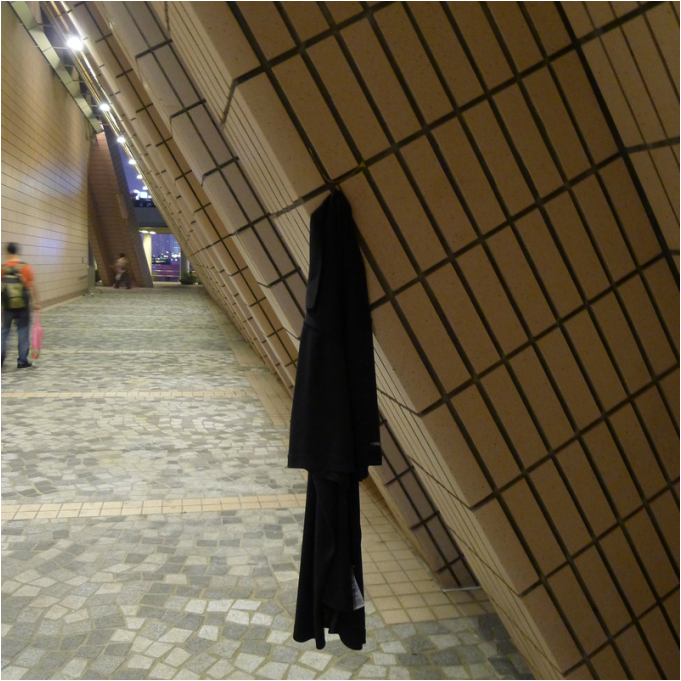
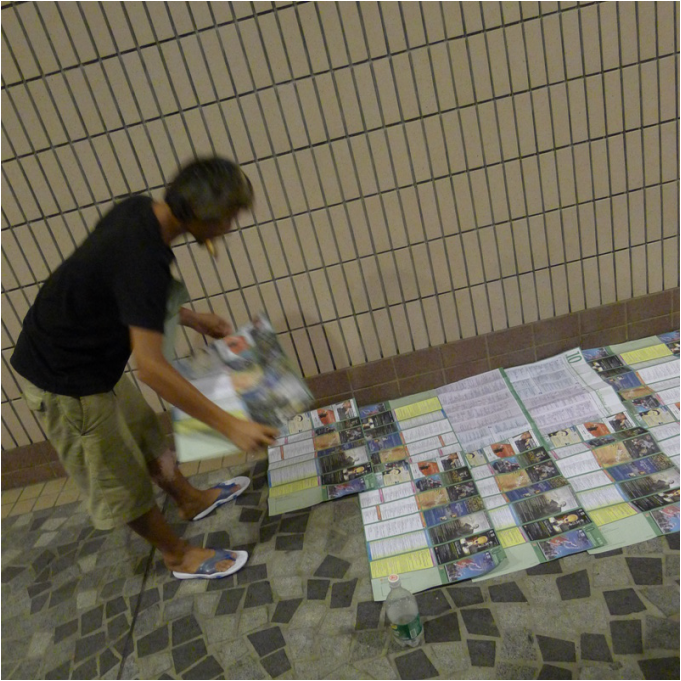
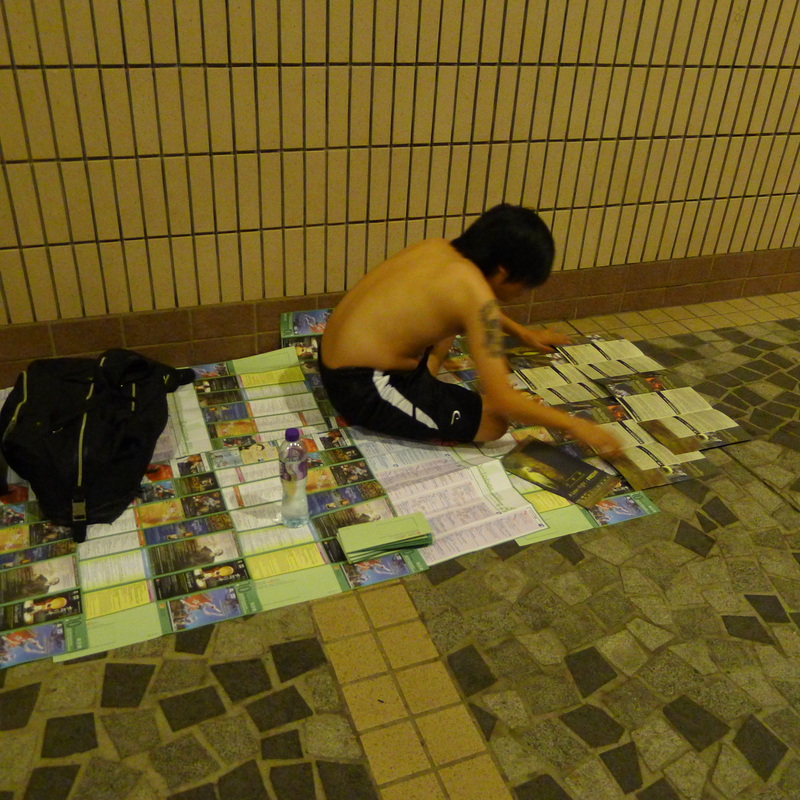
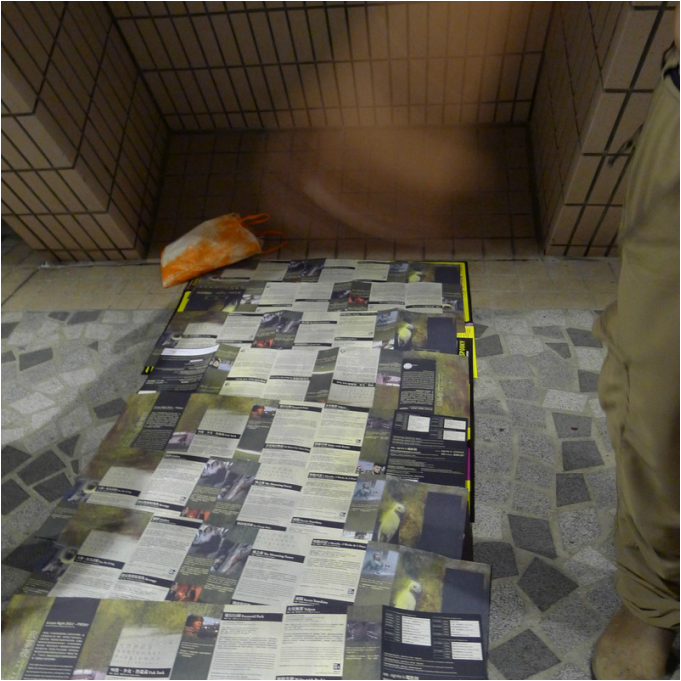
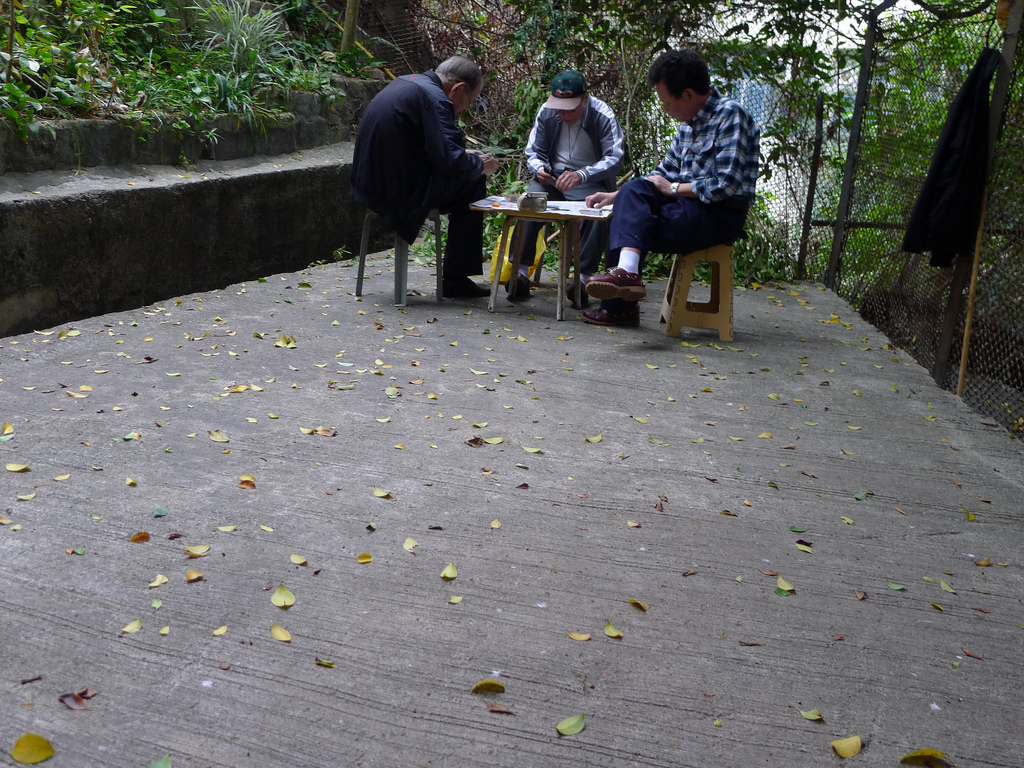
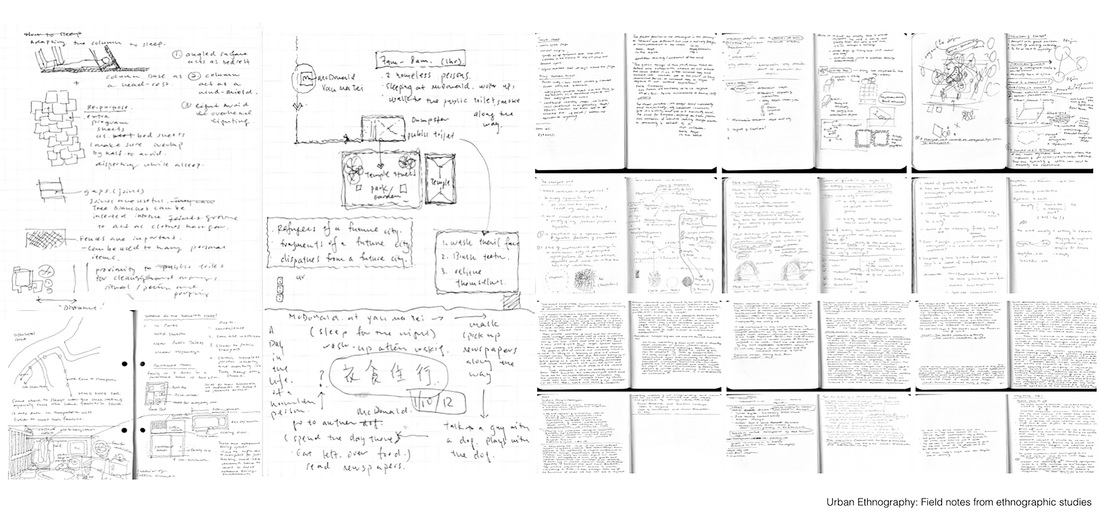
My recent work revolves around the term Lesser Urbanism. It is inspired by William Morris’s 1882 essay The Lesser Arts of Life. Lesser Urbanism curates, examines and presents aspects of urban life in high dense cities that are overlooked or ignored. Their presences are often negotiated, contested, and sustained along the margins of society. Although urban development is progressing at a relentless pace in Asia, I find there are still the vestiges of traditional rituals and local customs subsisting alongside and in quiet resistance against the process of globalization and gentrification. To disclose and celebrate these local cultures and alternative spatial practices where resourcefulness, creativity and sociability are called upon to overcome unfavorable situations and material scarcity is imperative in Asia, as more and more vernacular knowledge and places are erased and forgotten. My on-going research project on the Wah Fu informal public space in Hong Kong is one such effort. (http://www.studiochronotope.com/informal-religious-shrines-curating-community-assets-in-hong-kong-and-singapore.html). My interest in Lesser Urbanism transpires through a slow, deliberative journey reaching back to my early graduate work at Cranbrook, where I was concerned with the rules of forming and how elemental forms circumscribe space and propagates an emergent order through a bottom-up process of placement, aggregation, extension and configuration. In Lesser Urbanism, I am equally keen to articulate forms of individual and collective judgment and governance, both tacit and stated, as well as social conditions that give rise to, scale out and sustain localized spatial organizations. They herald a novel urban experience, alternative strategies of configuring spaces and make visible a vernacular poetics that are more representative of our contemporary splintered and tangled lives heightened by increasing contingency, scarcity and entropy. With the help of a social worker from the Salvation Army, I managed to interview a group of homeless residents who made the Cultural Center in Hong Kong their shelter for the night. " You can make a shirt hangar by using a twig. The gaps between the tiles are big enough to slot them into the space. But you need to use a fresh one and some efforts are needed to bend it to form a hook." "I use the old program pamphlets from the Cultural Center and spread them carefully over the floor. Important to have at least 2 layers to prevent the cold from seeping through. I overlap the pamphlets to make sure my 'mattress' is not scattered all over during the night. Don't worry, the pamphlets are for events that have already passed and we make sure they are disposed off in the morning. We don't want trouble from the authorities. We are also doing the earth a favor too by recycling these pamphlets!" "The columns of the Cultural Center are excellent for us. We can slide in-between the two columns and the angled floor is like pillow. I wonder if the architect thought of us when he designed the center?"
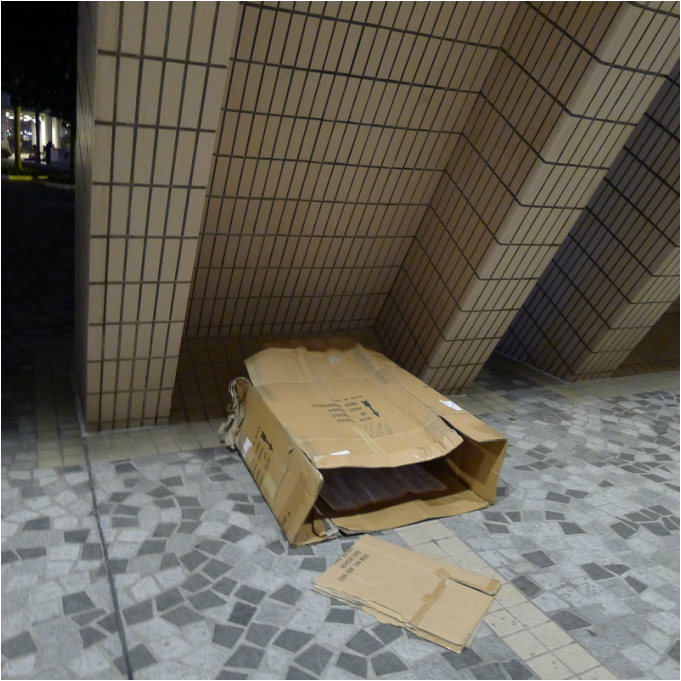
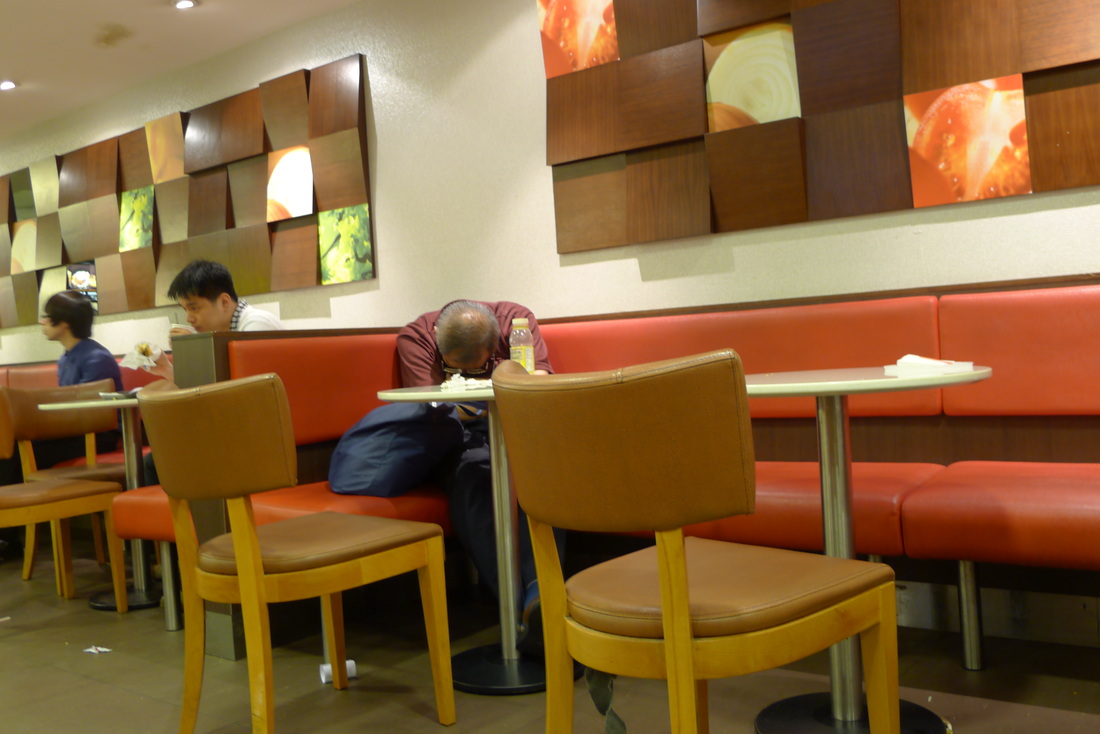
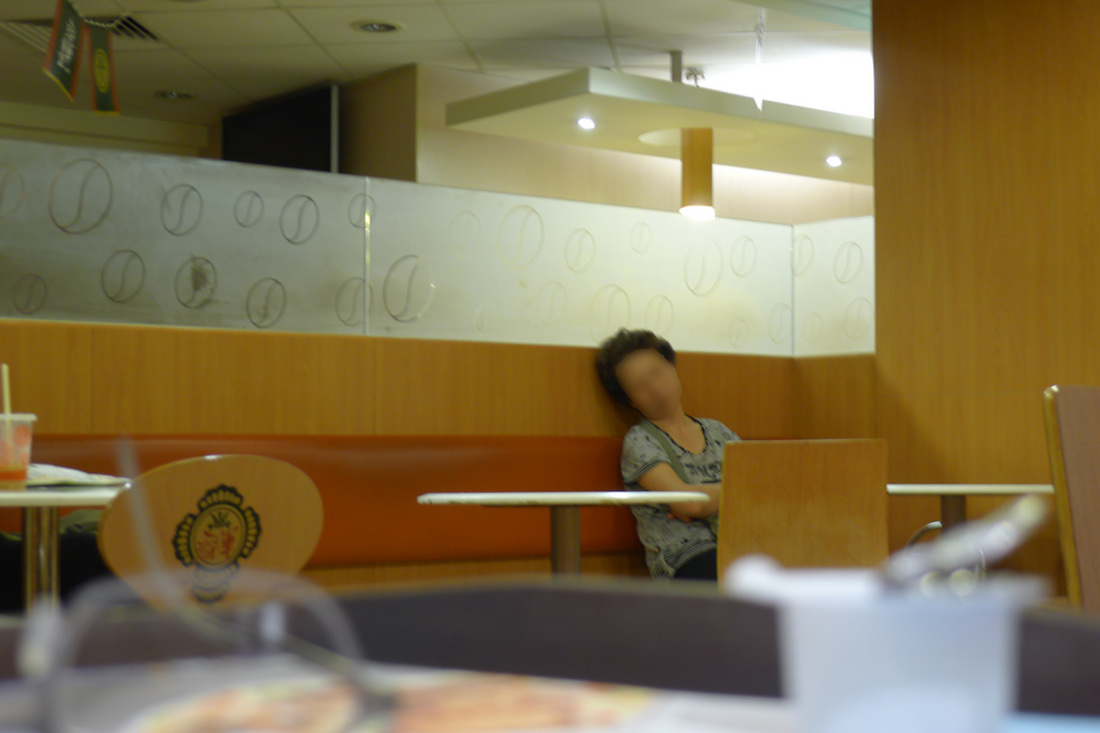
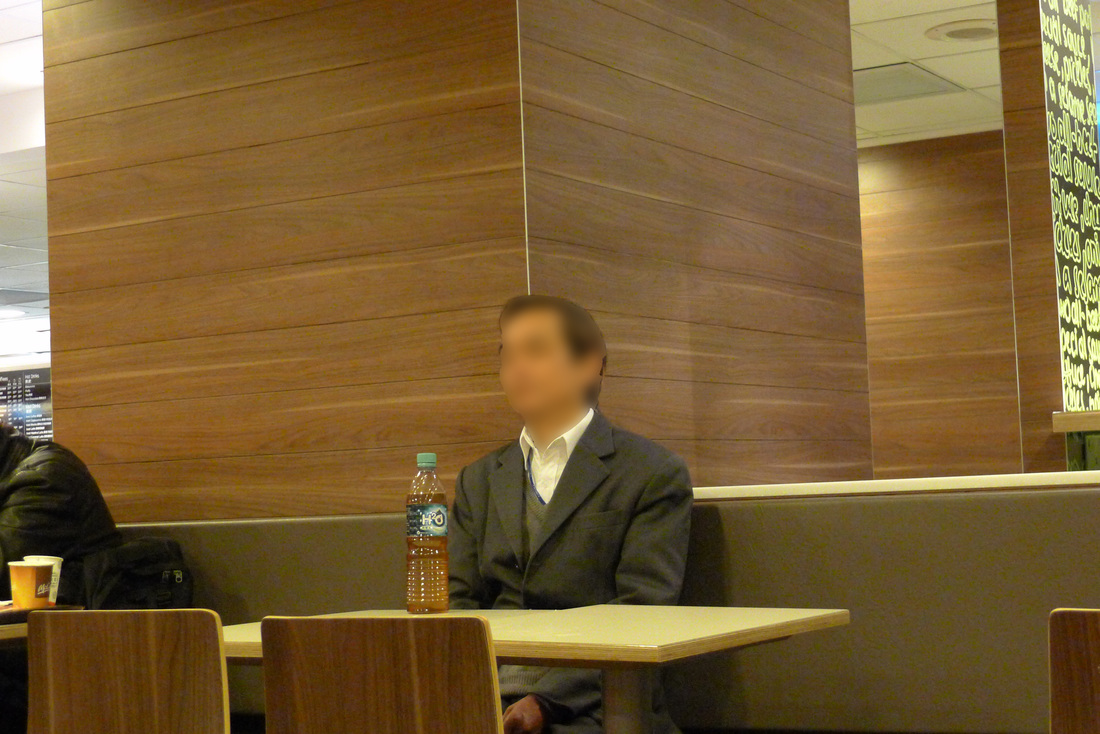
"If I'm in a hurry, I'll just take a medium size cardboard and slide my body inside. It's like a blanket. I'll sleep in-between the columns to get some protection from the wind. Most important of all is to protect your chest! I interviewed some Hong Kong residents who spent the night at McDonald's. They were an interesting group of individuals who, by choice or circumstance could be found in the 24-hr fast food restaurant for different lengths of time.
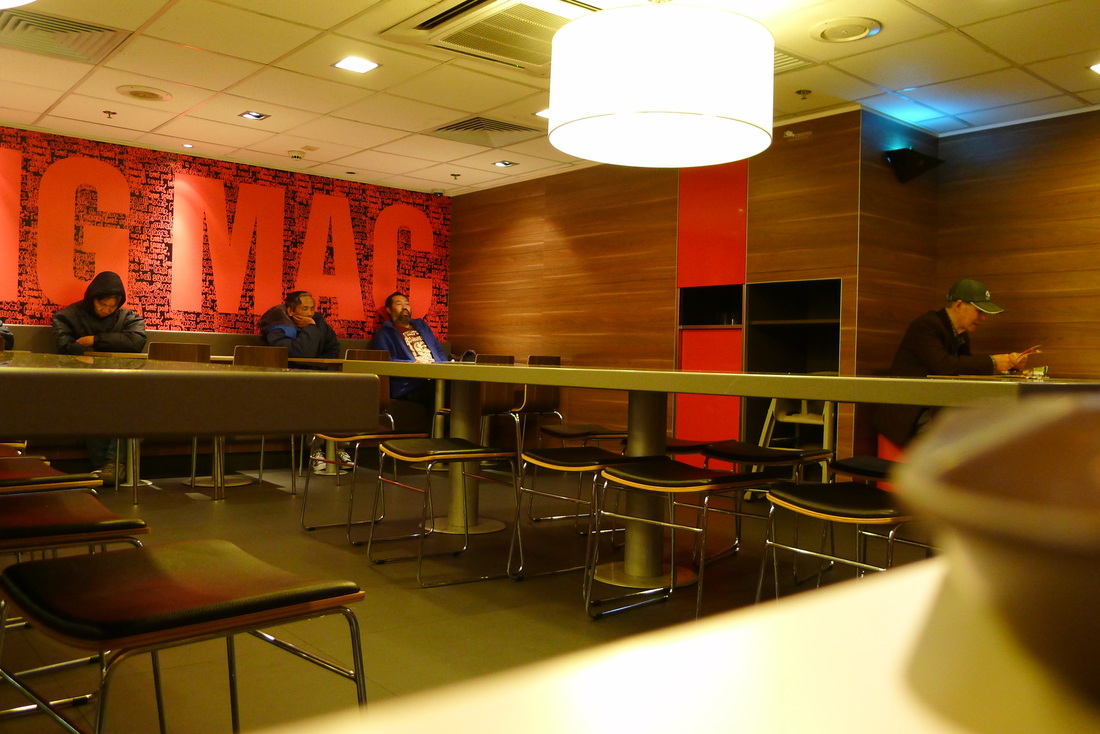
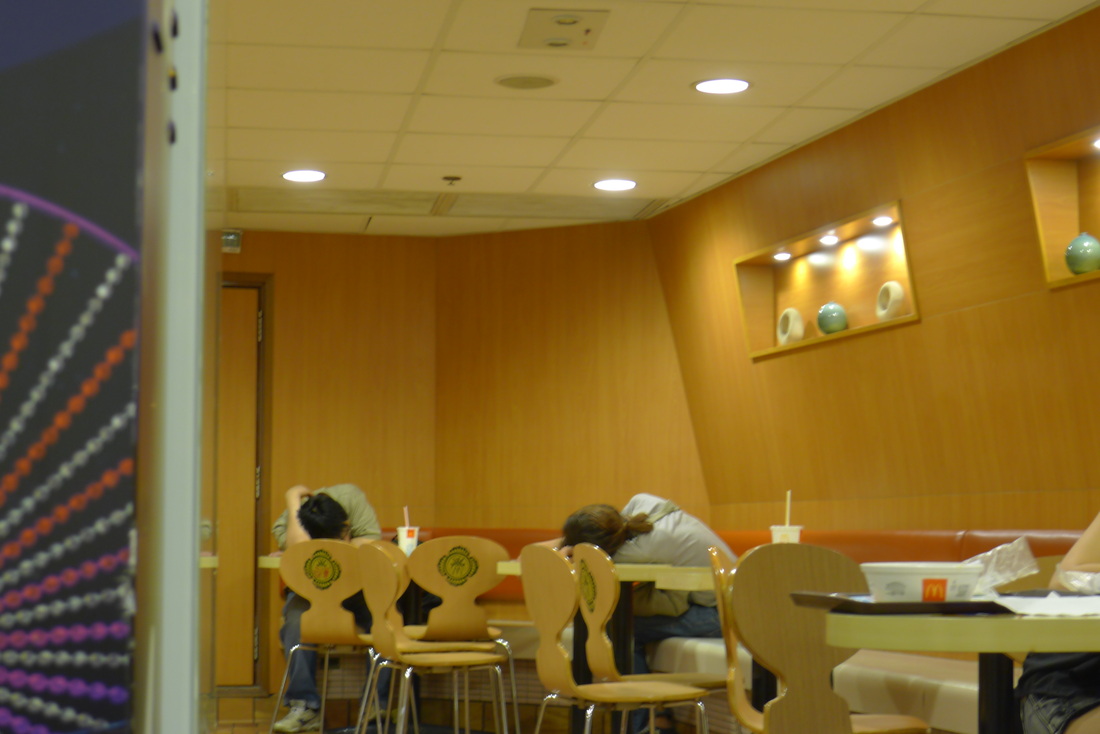
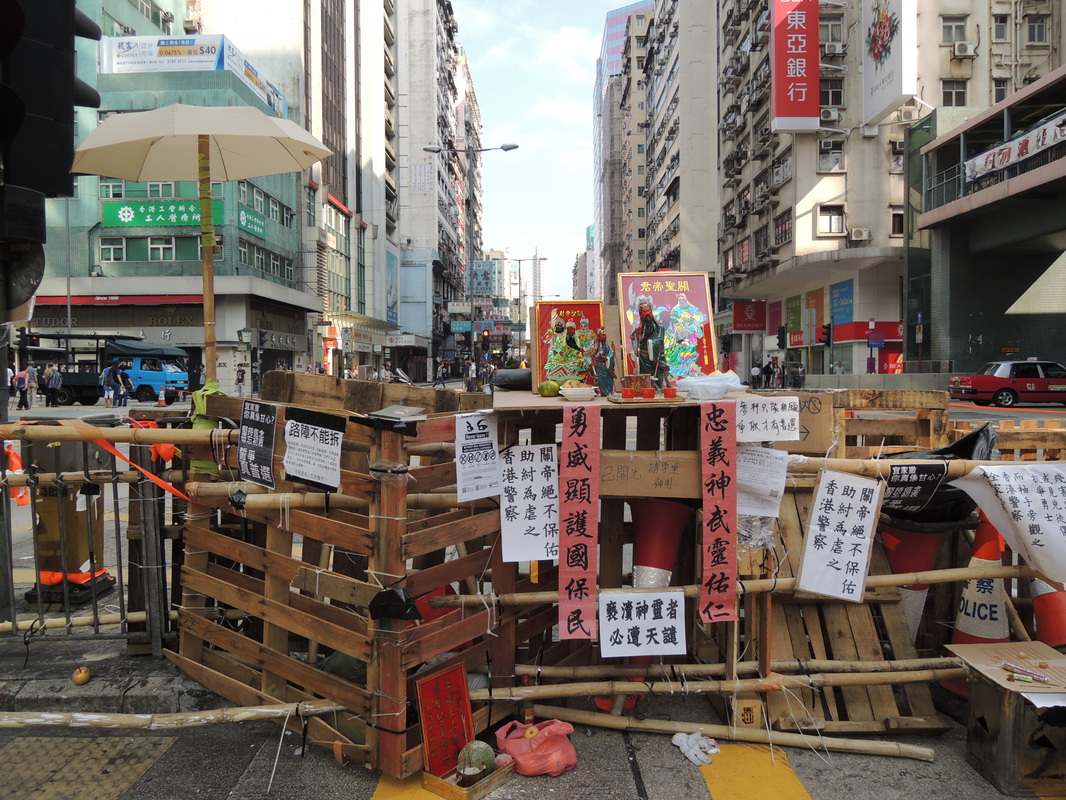
" I don't have a home. I usually spend my nights in the internet cafe if I get paid. There I can surf the web, chat online and eat noodles very cheaply. If I'm broke, it'll be the park or McDonalds." "I come here every night. It's cleaner and safer. I even see women sleeping here! And it's definitely warmer during the winter months." "Here I can get a cup of water from the counter staff. Some are nice as they know we have no money. But I also try not to create trouble." 'Why McDonald's? The use of the toilet of course. It's convenient especially for me. And I can also wash up in the morning" "I'm not here every night. I can't sleep so came here to get something to eat and read the newspaper." "Some staff can be quite mean. They will deliberately switched on the lights at the corner of the restaurant even though no one is around or they will put up some barrier to prevent us from using the space." "You need to know how to sleep here. If you lay your head on the table, they will come wake you up. So you try to sleep upright. Not easy but you get used to it." "I have a few McDonalds around the neighborhood where I go to each week. I try not to stay in the same restaurant every night because they may not like it. So I'll rotate my stay and so far it has been OK." "I just finished work, so came here for some food before going home. Yes, I see many who seem to be using this place to sleep. I'm fine as long as they are considerate. It's empty anyway." Professor Siu sent me this wonderful picture of an informal shrine set up by the protesters. He wrote, "The Guan Gong statue was worshiped by both the Police and the Triad Societies… And the citizens used this to counter their power against the protesters.
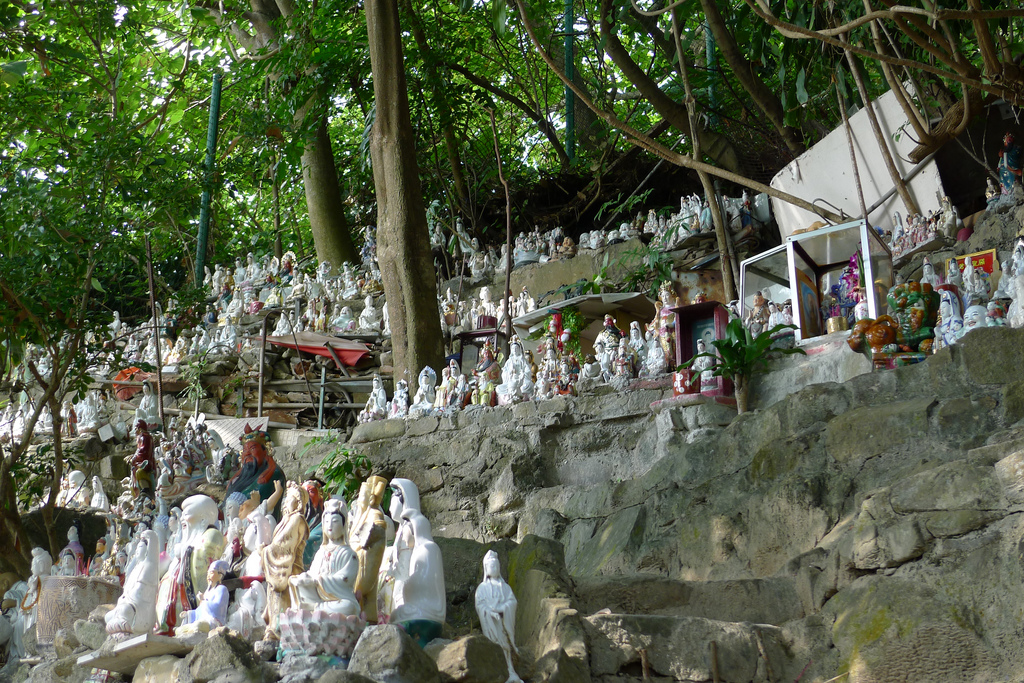
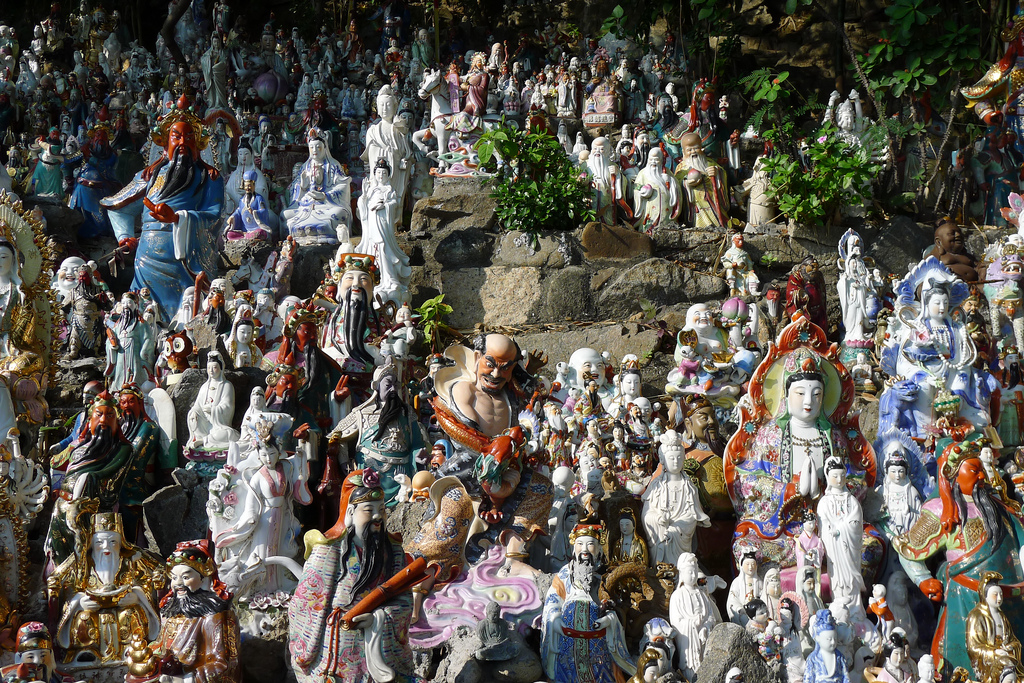
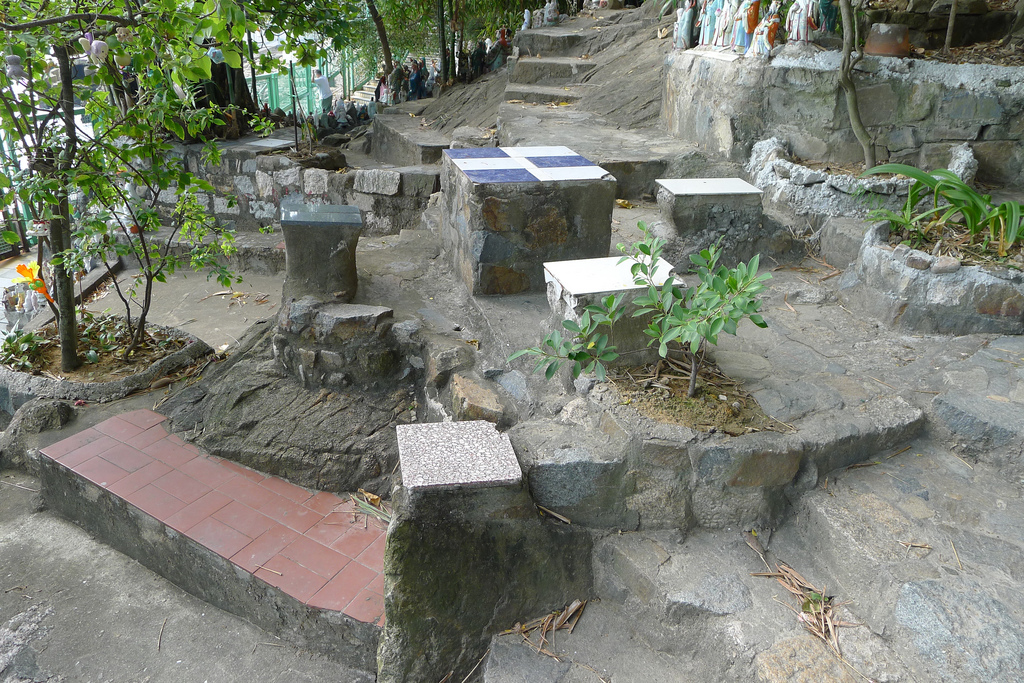
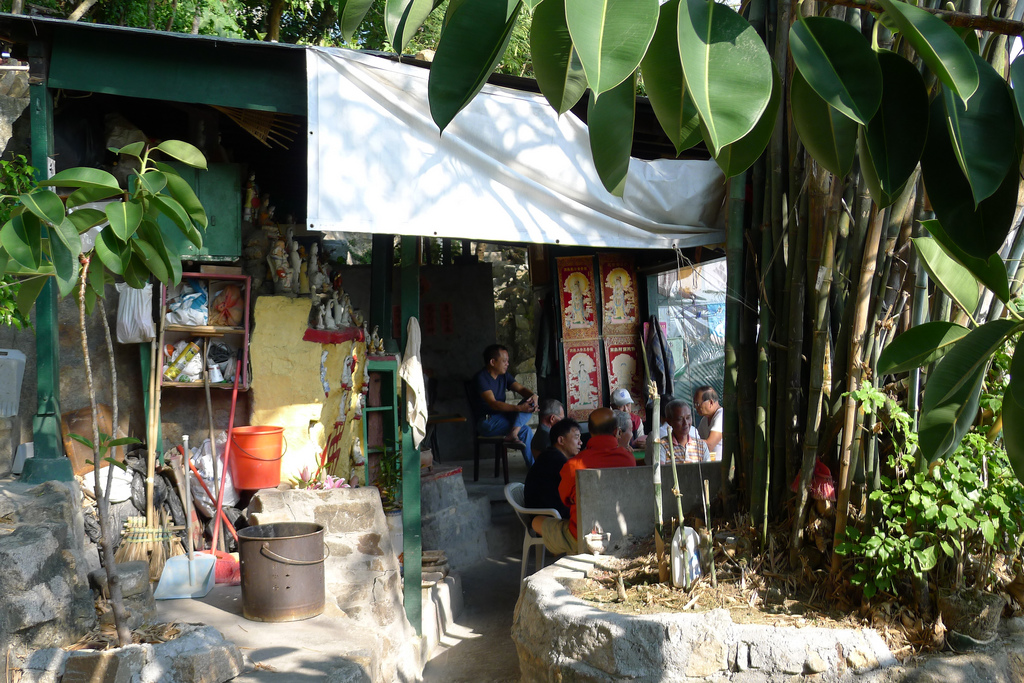
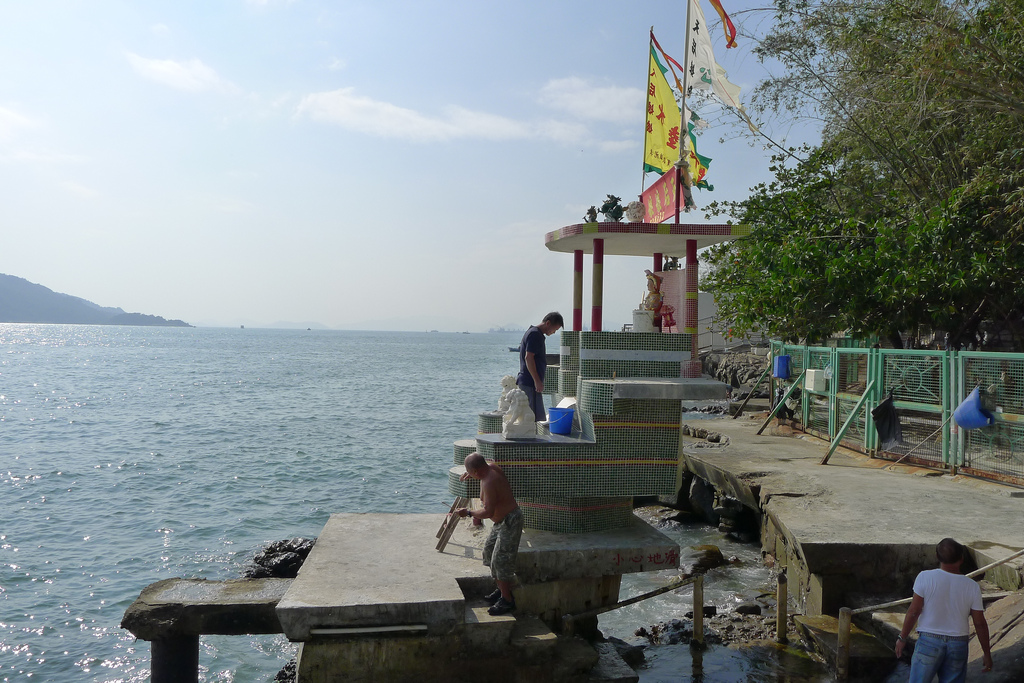
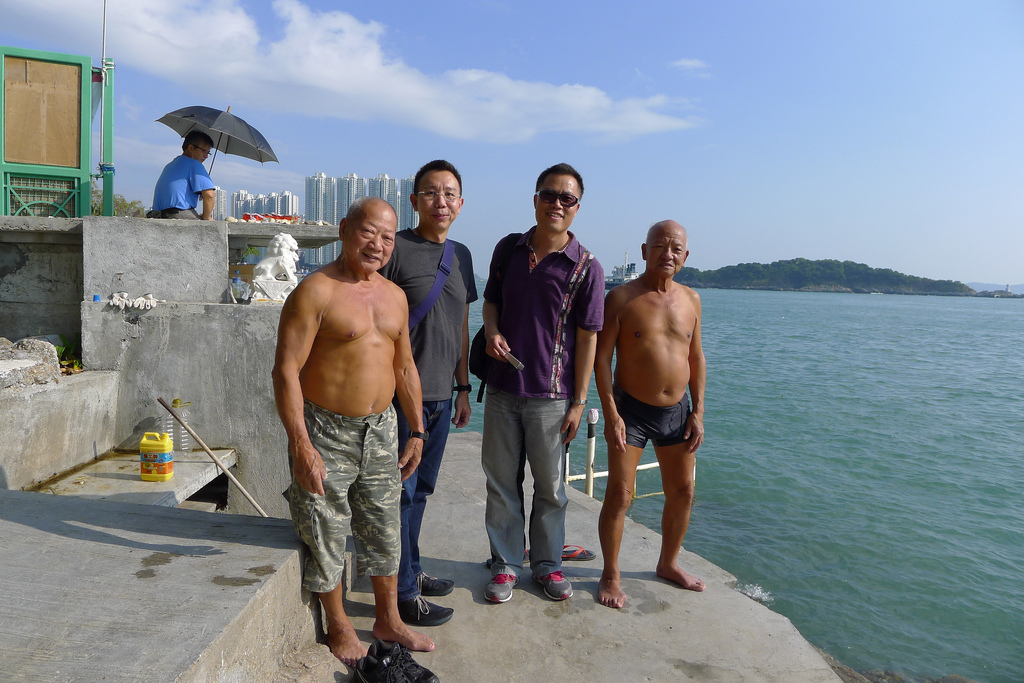
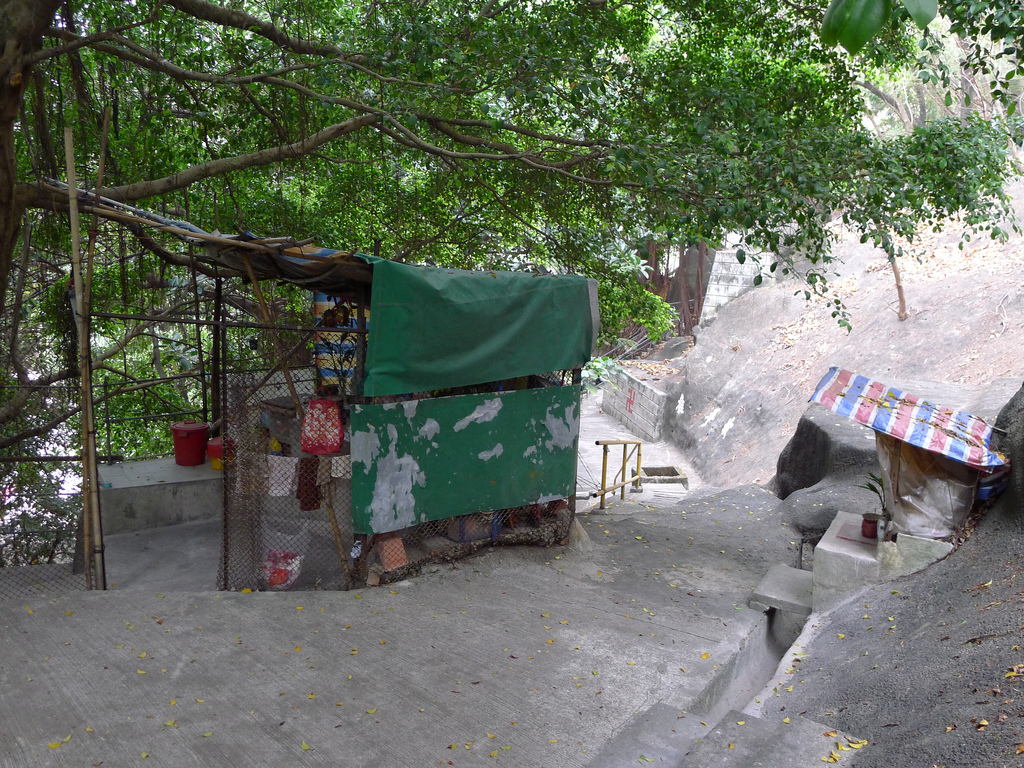
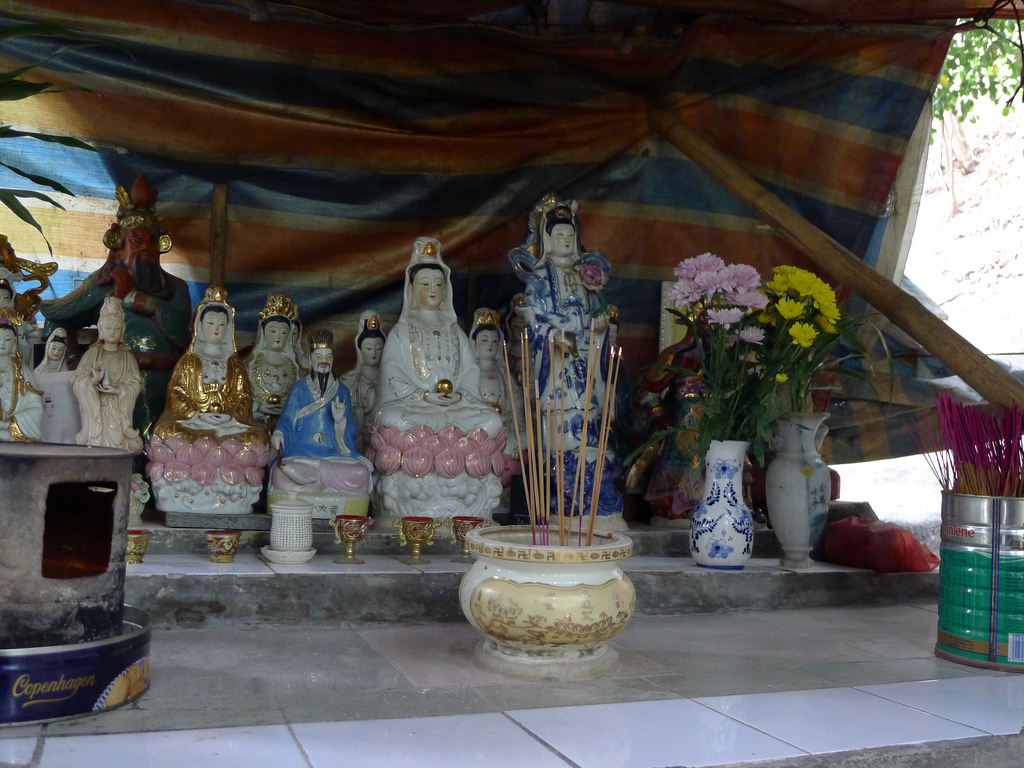
The story of the Wa Fu community space began almost 30 years ago. The place was a destination for residents living in the near by housing estate to leave their statues of porcelain deities when they relocated or when the religion was no longer practiced by the younger generation after the passing of the elderly family member. The stepped profile of the ground leading to the sea is an ideal site to place the deities. They are secured individually by a layer of cement to prevent them from toppling over during a typhoon. Through time, a sea of porcelain deities slowly emerges and are they cared for by a group of elderly residents. Some deities are protected by simple shelters while others share their spaces with toy figurines that were also left here. A self-constructed shelter serves as both a community space for the elderly and for them to keep their belongings. A well close-by provides fresh water for cleaning after taking a dip in the sea. We were told it is a popular activity among the elderly and younger residents. Some come for a swim early in the morning before heading off to work.
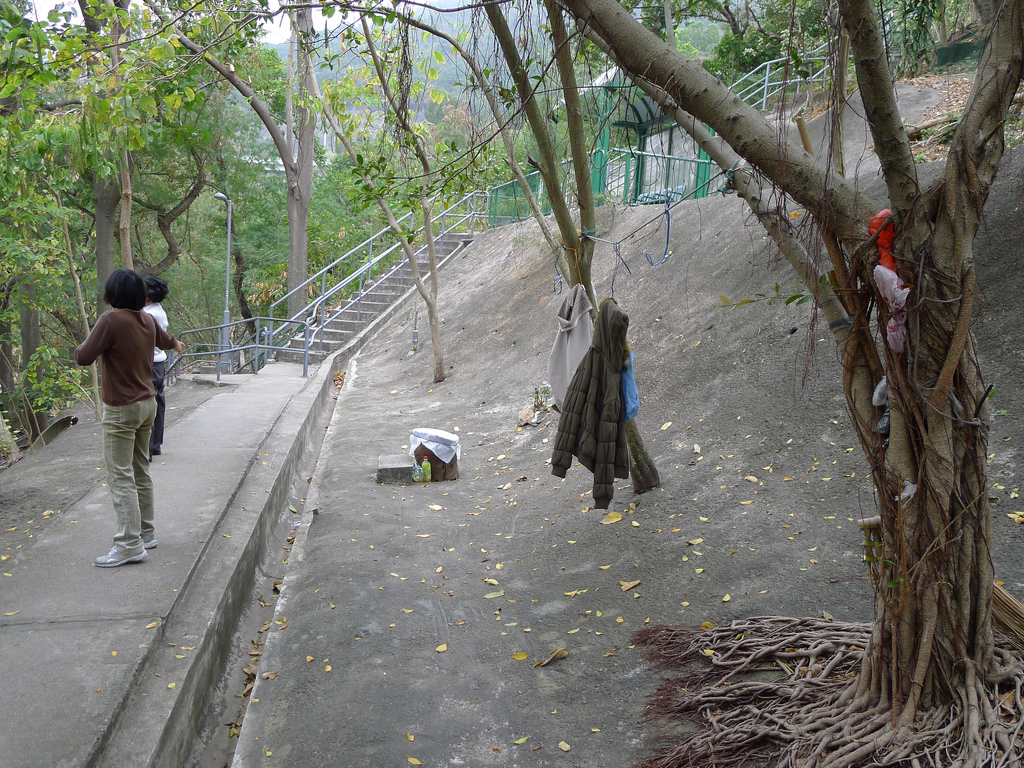
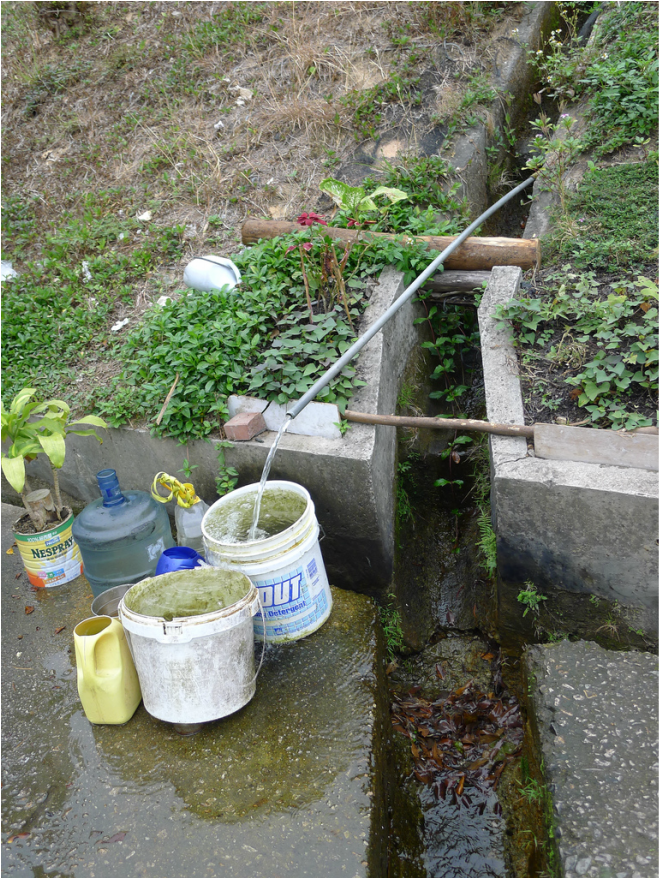
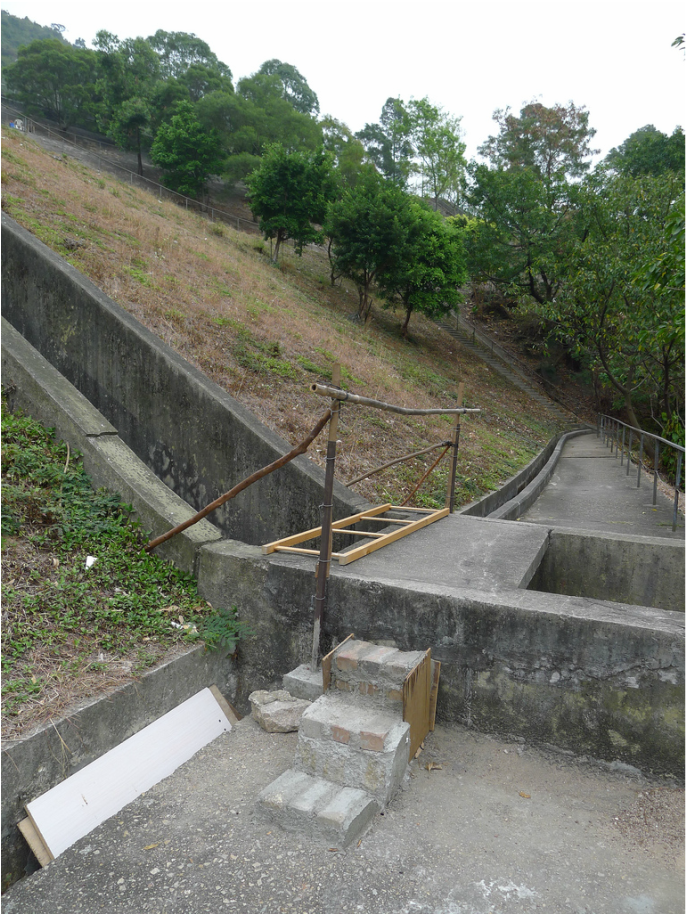
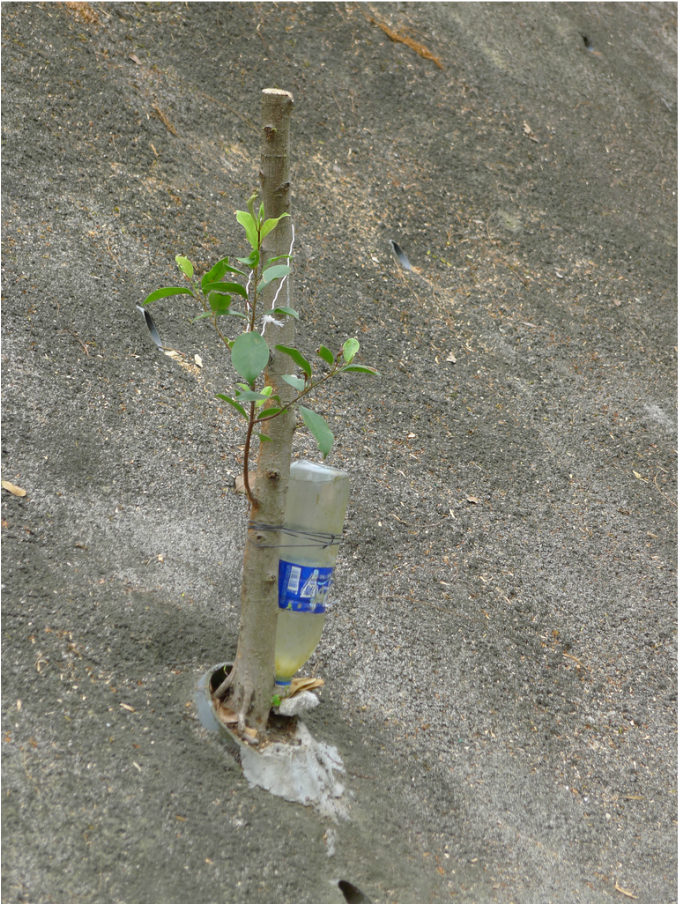
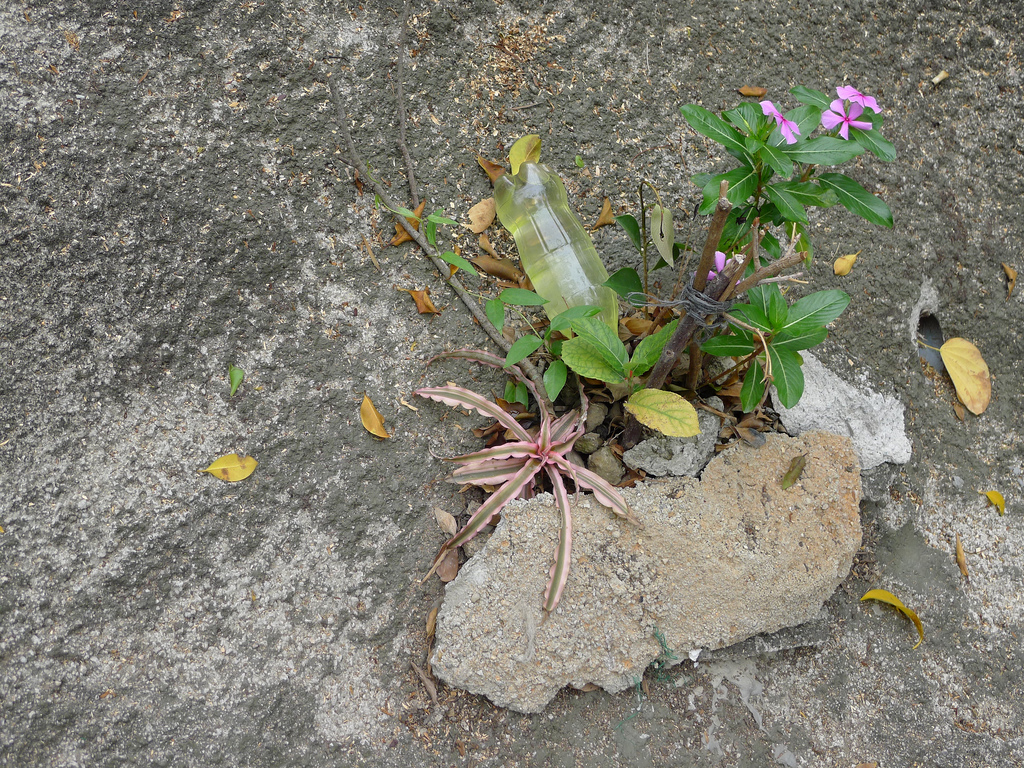
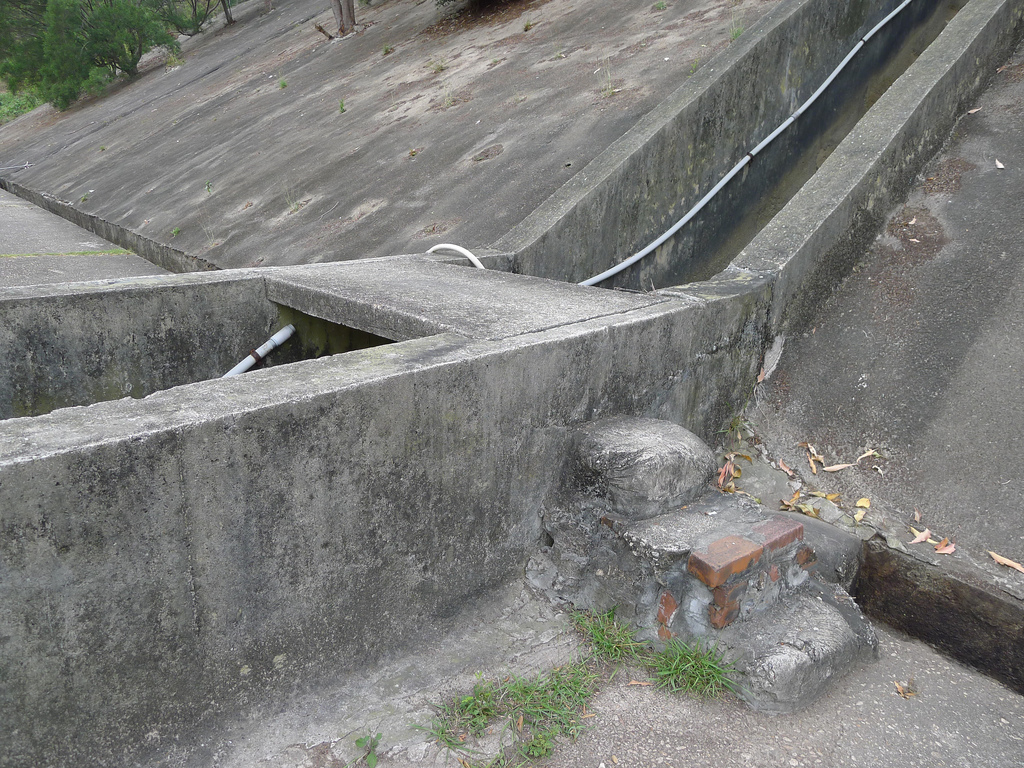
The hillside informal shrine in So Uk Estate is connected to a larger network of elderly walkers and informal social spaces. The shrine is situated along a path that winds up the hillside, which is a favorite spot for the mostly elderly residents and housewives to engage in their morning walks and exercises. The shrine is often a stop over for the residents. They would offer incense or a simple prayer at the shrine on their way up or down the hill during their morning exercise routines. Besides exercising, the residents have also undertaken small, self-initiated actions along the various exercising spots; such as plant caring, building of small concrete steps to link disconnected parts of the hillside and allow a safer walk up the hill, introducing resting spots, setting up support facilities for the morning exercises, and repairing broken planters. Water for the plants is collected from the natural run-offs from the hill in small pails and buckets. The So Uk Estate shrine and the adjacent exercising spots are excellent examples of bottom-up initiatives in place-making. It makes a strong case for allowing urban dwellers to take control and have the opportunity to shape their immediate spaces in the city rather than top-down initiatives that often miss the point and cost much more than they should be.
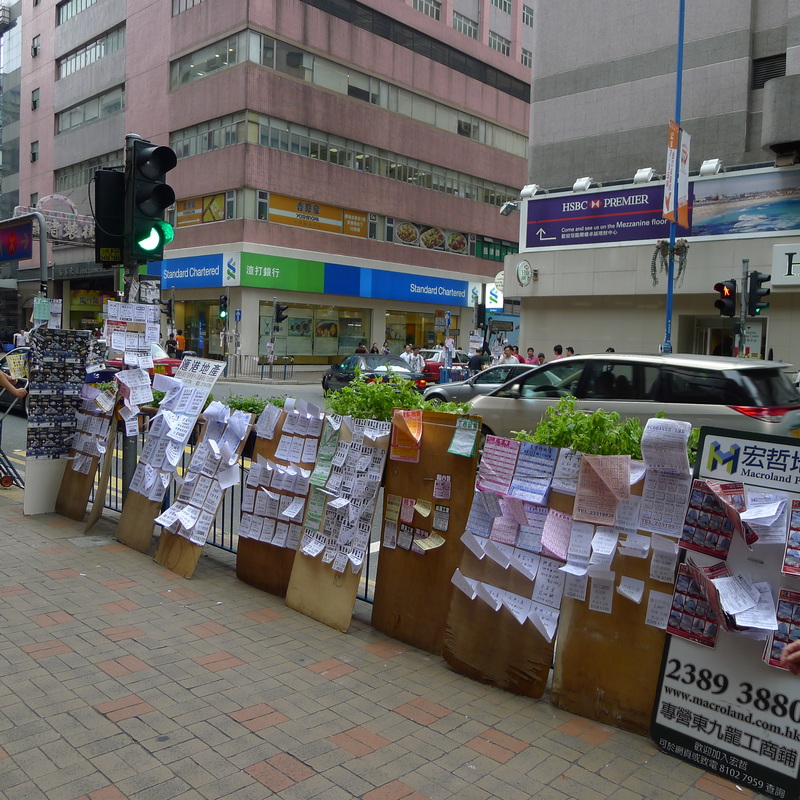
Strategically placed street advertisements along a sidewalk and crosswalk in Hong Kong. The steel barriers are re-purposed as supports for the advertisement boards.
|
Archives
August 2023
Categories
All
|



























































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
